Solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries and their main application in EV
Conventional lithium-ion batteries are a proven and ubiquitous technology that uses a solid, porous separator soaked in an organic liquid electrolyte to shuttle charges between electrodes for energy conversion and storage. These electrolyte solutions provide high conductivity and excellent electrode surface wetting. However, liquid electrolytes based on highly volatile and flammable organic solvents also have some well-established drawbacks, including low ion selectivity, poor long-term stability, and, most importantly, safety issues. Solid-state lithium batteries replace the electrolyte-soaked separator with an ionically conductive solid, thereby eliminating the liquid electrolyte altogether. In comparison, all-solid-state lithium batteries mitigate the persistent issues posed by conventional liquid electrolytes, particularly safety and long-term electrochemical and thermal stabilities. In doing so, solid-state batteries also provide improved energy & power densities via combination with high-capacity, high-voltage electrode materials, and reduced need for packaging and state-of-charge monitoring circuits, thereby improving capacity and charging speeds while potentially reducing production costs.
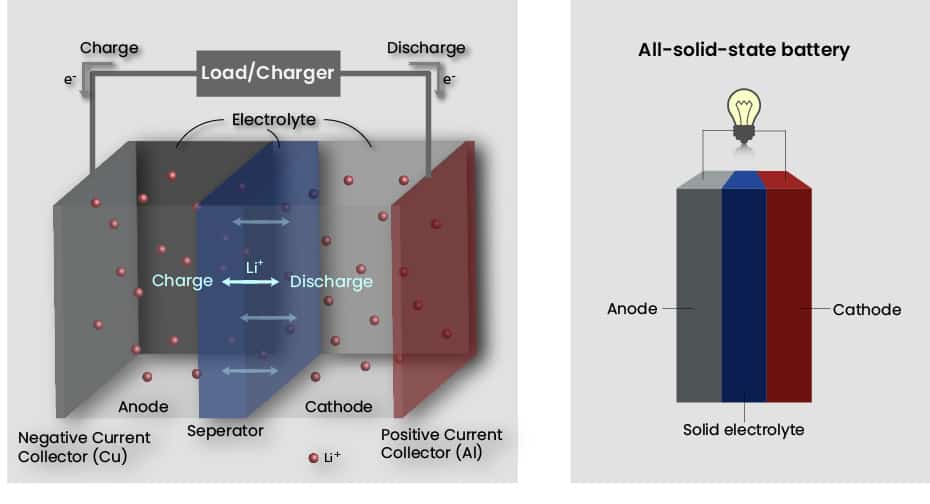
Solid-state battery applications

EV adoption
Download the FOM Technologies Product brochure
Fill in your information and click download to access the pdf.
